Radon Decaying To Polonium In Humans #3

by Mikkel Juul Jensen / Science Photo Library
Title
Radon Decaying To Polonium In Humans #3
Artist
Mikkel Juul Jensen / Science Photo Library
Medium
Photograph - Photograph
Description
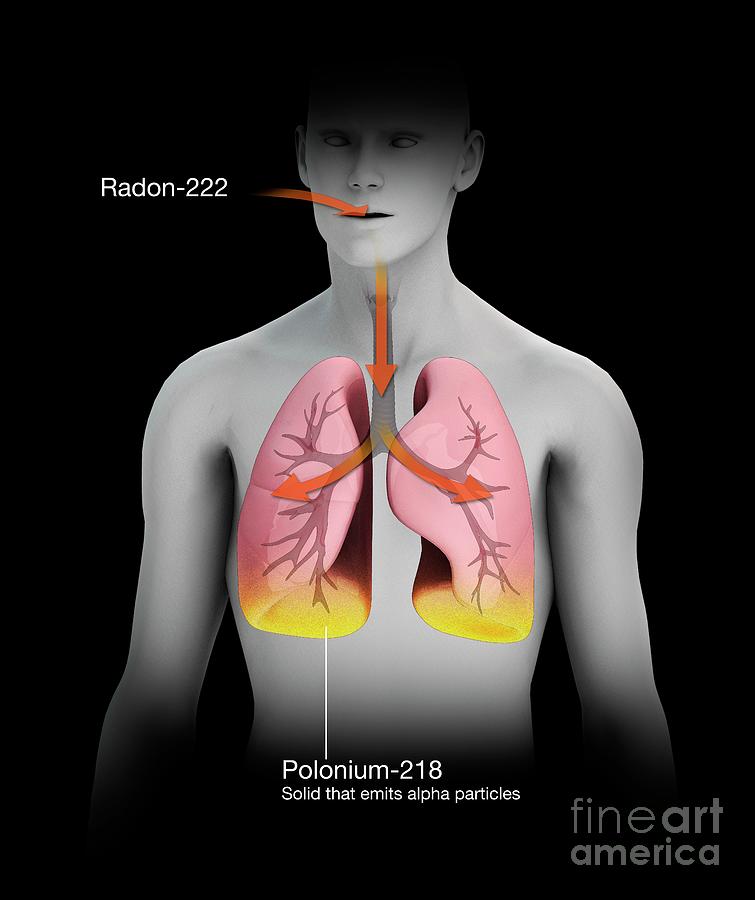
Radon decaying to polonium in humans, illustration. Radon is a chemical element that is a radioactive gas that occurs in nature. It is being continuously generated from radioactive isotopes in the Earth's crust. The most stable isotope of radon is radon-222, which has a half-life of 3.8 days. As a gas, it can be inhaled into the lungs where it decays via alpha particle production to produce polonium-218, a solid that has a half-life of just over three minutes. Further decay takes places, eventually producing a stable isotope of lead. The effects of this can lead to an increased risk of lung cancer. For this illustration without labels, see image C047/4524.
Uploaded
February 23rd, 2021
Statistics
Viewed 366 Times - Last Visitor from Ottawa, ON - Canada on 04/25/2024 at 2:15 AM
Embed
Share
Sales Sheet
Comments
There are no comments for Radon Decaying To Polonium In Humans #3. Click here to post the first comment.






































